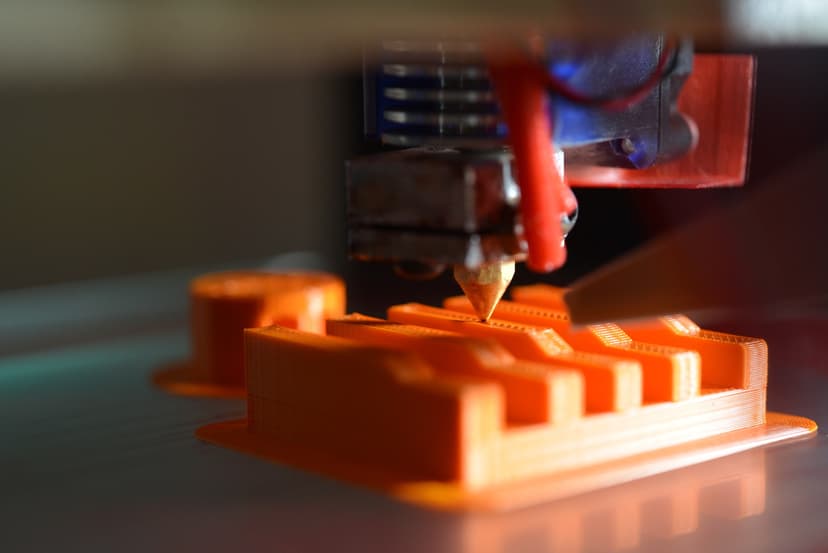
Stereolithography (SLA) is an additive manufacturing process that utilizes a liquid photopolymer resin to create intricate and precise three-dimensional objects. By selectively curing and solidifying the resin layer by layer using a focused UV laser, SLA achieves exceptional detail and surface finish.
The SLA Process:
- A digital 3D model is created using CAD software, and it is saved in STL format, which is compatible with SLA printers.
- Slicing software is utilized to divide the 3D model into thin, horizontal layers, generating instructions for the SLA printer.
- A liquid photopolymer resin is chosen based on the desired properties, such as mechanical strength, transparency, flexibility, or heat resistance.
- The SLA printer's vat is filled with the selected resin, ensuring proper positioning of the build platform.
- The build platform is lowered into the resin, and a focused UV laser selectively cures the first layer based on the sliced data.
- The build platform gradually rises, separating the cured layer and allowing the resin to flow back for the next layer.
- The SLA printer continuously scans and cures each subsequent layer, incrementally raising the build platform until the object is fully formed.
- Once the printing is complete, the object is carefully removed from the vat and rinsed in a solvent bath to remove excess uncured resin.
- To achieve the final strength and material properties, the printed object undergoes post-curing using UV light or a specific curing chamber.
- Additional steps, such as removing support structures, refining surface finish, or applying coatings, can be performed if needed.
Advantages of SLA:
- High Resolution: SLA delivers exceptional detail and surface finish, suitable for intricate and visually appealing objects.
- Material Choices: Choose from a wide range of photopolymer resins with different mechanical properties and characteristics.
- Smooth Surface Finish: SLA prints have minimal visible layer lines, resulting in polished and smooth surfaces.
- Accuracy and Precision: SLA offers high dimensional accuracy, making it ideal for applications with tight tolerances.
- Support Structures: SLA printers generate easily removable support structures for complex geometries.
Disadvantages of SLA:
- Limited Print Size: SLA printers typically have a smaller build volume compared to other 3D printing technologies.
- Post-Curing Process: Objects printed with SLA require additional time for post-curing to achieve their final strength and stability.
- Cost: SLA printers and materials can be more expensive compared to other 3D printing methods.
Applications of SLA:
- Prototyping: SLA is widely used for creating high-resolution prototypes in automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods industries.
- Jewelry and Art: SLA's precision and smooth surface finish make it popular for producing intricate jewelry and artistic pieces.
- Dental and Medical: SLA is employed for producing dental models, surgical guides, custom prosthetics, and anatomical models.
- Engineering and Product Design: SLA enables engineers and designers to iterate and test designs before mass production.
- Microfluidics: SLA is utilized in fabricating microfluidic devices for biomedical research and diagnostic applications.